What is DTF?

DTF stands for Direct-To-Film printing, an innovative and evolving printing technology that enables the printing of high-resolution images on PET film and transferring prints onto textile surfaces. This process involves using specialized inks and adhesive materials to transfer the design onto fabric. It is important to note that in this process, the film is only the ink carrier and is not part of the print. It is worth mentioning that DTF prints, unlike other forms of textile printing, can achieve photographic quality.
Before delving deeper into the DTF process, it is important to understand that this is not another generation of iron-on transfers from the past. Although these technologies may seem similar at first glance, DTF is an entirely different technology that surpasses many currently used textile printing methods in terms of durability and precision.
Below you will find a detailed description of each stage of the DTF printing process.
Pattern Creation and DTF Printing
The process begins with the creation of the desired pattern, which will be transferred to the fabric in the following steps. For this purpose, the design is developed using graphic design software such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or Affinity Designer. It is important to note that the project should be created in the CMYK color space to ensure accurate color reproduction in the print compared to what is seen on the screen, and it should have a resolution equal to or higher than 300 dpi. This is crucial to achieve high quality and detail in the final print.
After creating the graphic design, the next step is to use RIP (Raster Image Processor) software to print the prepared graphic. RIP software plays a crucial role, managing not only the color layer of the print but also the white layer. This tool allows precise control over the printing process, adjusting resolution, and controlling the amount of white ink and print detail. Examples of RIP software include AcroRIP, CADlink, or Flexiprint.
Printing
During the DTF printing process, two layers are used: the color layer and the white layer. The color layer contains special DTF inks that faithfully reproduce the graphic design and effectively adhere to and penetrate the adhesive surface of the DTF film.
The white layer not only enhances the color intensity, especially on black fabrics but also adds flexibility to the print. It is thanks to the white DTF ink that the print remains durable, flexible, and resistant to cracks. Additionally, the white layer plays a significant role in preparing the print for the subsequent stages of the DTF process. It serves as a base to which the DTF powder will be attached in later stages, crucial for the permanent transfer of the pattern to the fabric. It is important to note that controlling the amount of white ink is essential, as a higher amount can improve the durability and color intensity but may affect the thickness of the print and its negative reception by the customer.
It is important that the white DTF ink has good coverage and high efficiency. This makes prints more economical as less ink is consumed. At the same time, with high whiteness intensity, greater saturation of CMYK colors can be achieved on dark and colored fabrics, with a simultaneous reduction in the thickness of the white layer.
Various types of inks are available on the market, but finding ink with good coverage and true, non-bleeding white can be challenging. Our premium white DTF ink stands out with excellent coverage and whiteness intensity, allowing for not only cost-effectiveness but also exceptional color saturation of CMYK with less ink consumption and a simultaneous reduction in print thickness.

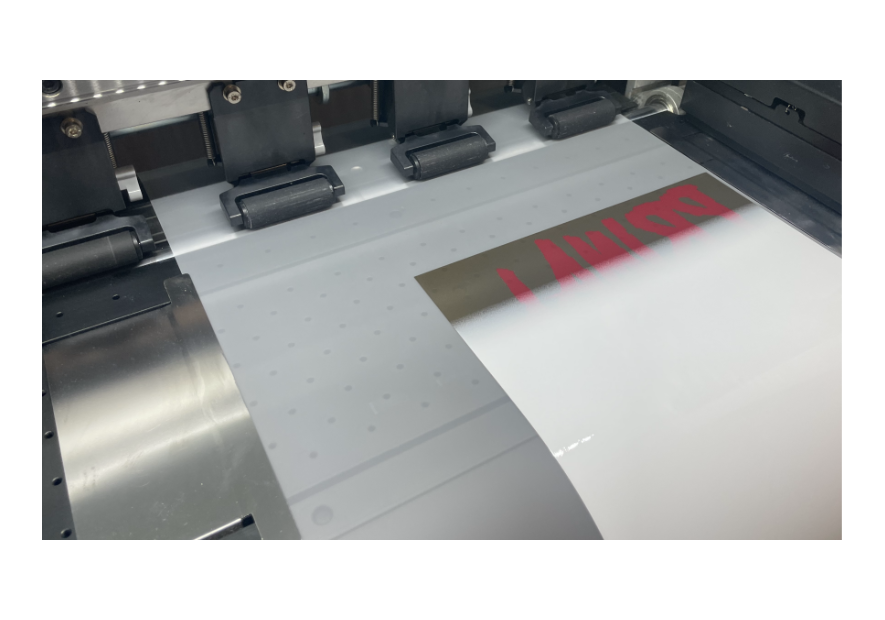
DTF Powder Application
After the printing process is completed, a special DTF powder is applied to the printed pattern. The DTF powder serves as an adhesive, which will permanently bond the print to the fabric in subsequent steps. This powder is also crucial for the durability and flexibility of the print. The elastic properties and softness of the print in touch largely depend on the type of adhesive powder used. The choice of the right powder and grain size is essential for the final result, as it determines the degree of flexibility and comfort of use of the print on textiles.
We offer several types of polyurethane (TPU) DTF powders in our store. Fine-grain with a size of 0-80 μm works well for filling in details. Elastic with a grain size of 80-170 μm is ideal for prints on T-shirts. Coarse-grain with a size of 120-250 μm, although this size is standard in other stores, we offer it as coarse because it creates a moderately thick layer, making it ideal for gluing prints on thick materials that require more adhesive (e.g., jeans).
It is worth noting that the powder adheres perfectly to the white ink due to the additives it contains. The composition of white ink includes substances (such as glycerin, titanium dioxide, urethane and vinyl resin, and drying accelerators) that promote effective adhesion of DTF powder. The inks permanently bond with the adhesive powder during the curing process.
After applying the powder to the still moist print, it is necessary to remove excess powder from the unprinted areas. This can be done by manually shaking the film or using a special powder shaker that will do it automatically.
Removing excess powder is essential because, in the final stage, after the print is heated into the fabric, the adhesive may be visible in unprinted areas. Shaking the film eliminates this problem.
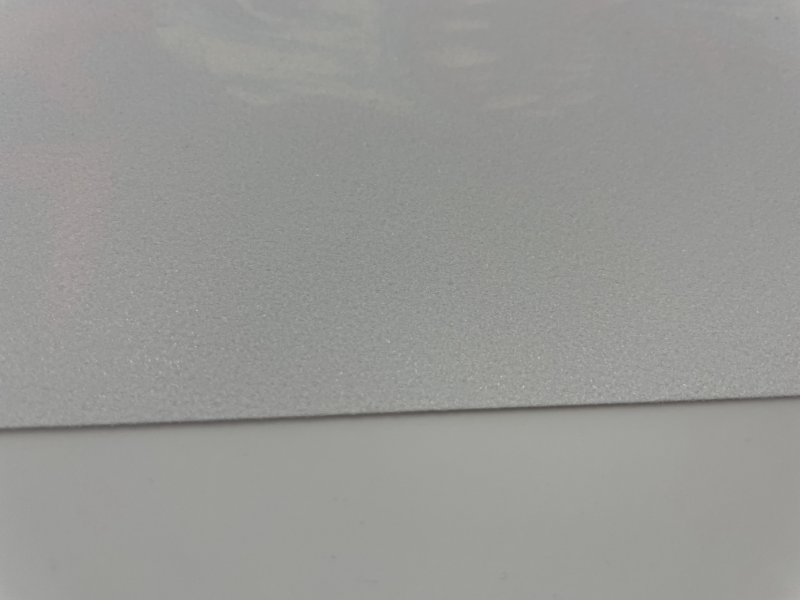

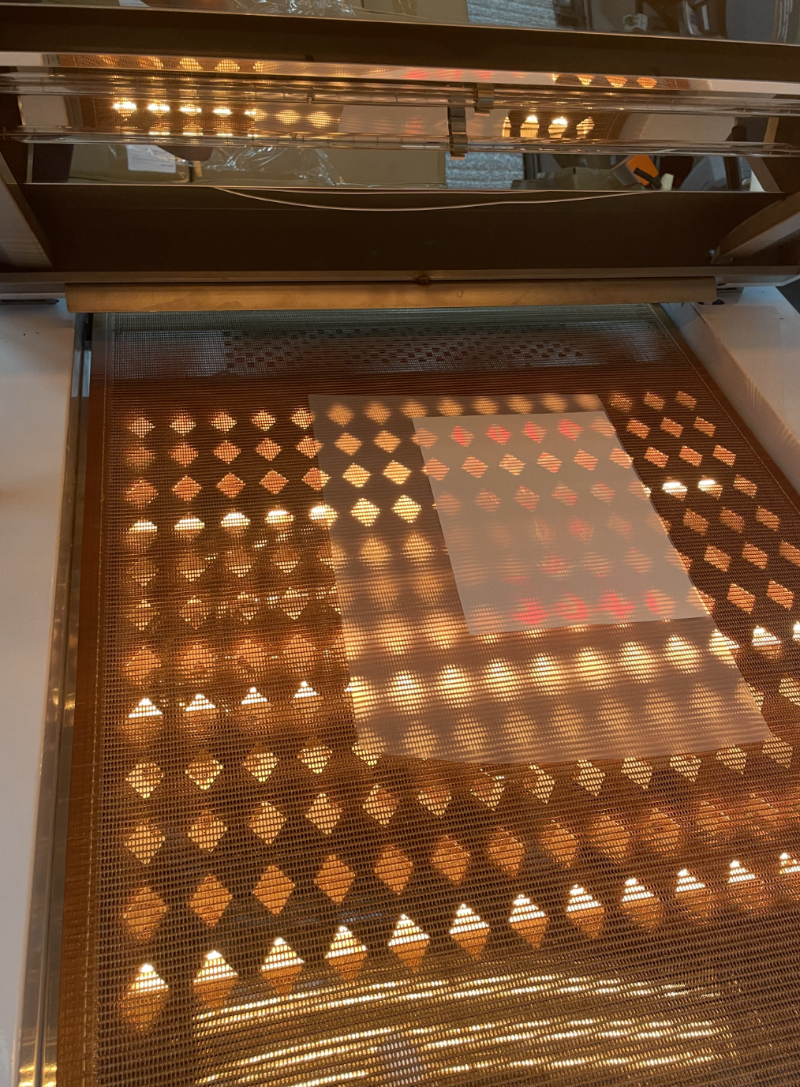
DTF Powder Melting
The film with the printed and powdered pattern goes through the melting process. The powdered print is placed in a DTF oven or a special drying tunnel, where under the influence of temperature, the powder melts across the entire surface. This process aims to remove moisture from the print and melt the adhesive, which permanently bonds with the DTF inks. The components in the ink facilitate the effective bonding with the DTF powder.
The final result is a durable, flexible, and high-quality print. After glazing and drying the melted powder, the print is fully prepared for transfer to the chosen material.